Environment Setup
|
This tutorial was developed and tested with:
|
Workshop Tools
The following tools are required to run the exercises in this tutorial. Please ensure that they are installed and properly configured before proceeding with any of the tutorial chapters.
| Tool | Reference |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The extensions source code used during this workshop can be found at the following URL: https://github.com/aolle/rhbk-workshop/code |
Deploying Red Hat build of Keycloak on OpenShift
Deploying Red Hat build of Keycloak on OpenShift using the Operator
-
Open a browser window and log in to the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform web console.
-
From the Administrator perspective, click
Operators, thenOperatorHub. -
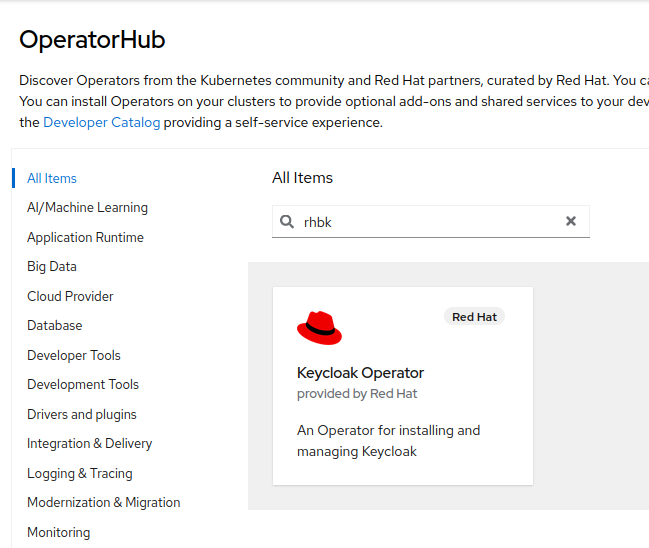
In the Filter by keyword field, type
rhbk.
-
Select the
Keycloak Operatortile and click Install.

-
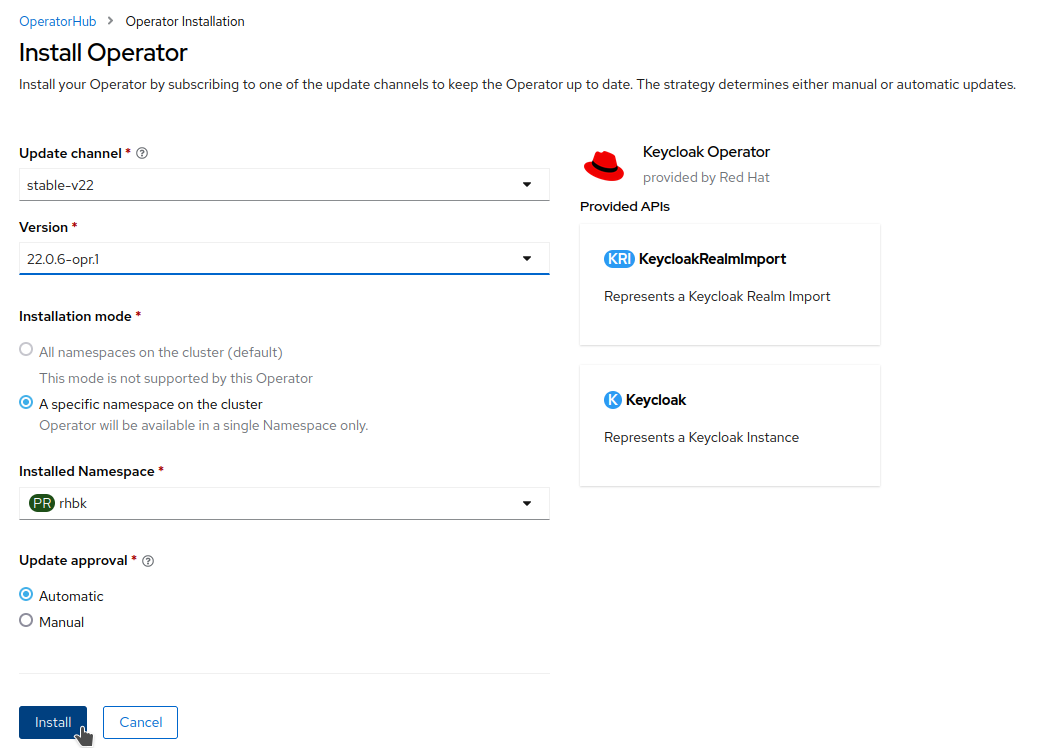
On the Install Operator page, keep the
stable-v22option from the list of available Update Channels. The Operator only supports the installation mode A specific namespace on the cluster. Create therhbkproject and choose Automatic update approval.
-
Click Install.
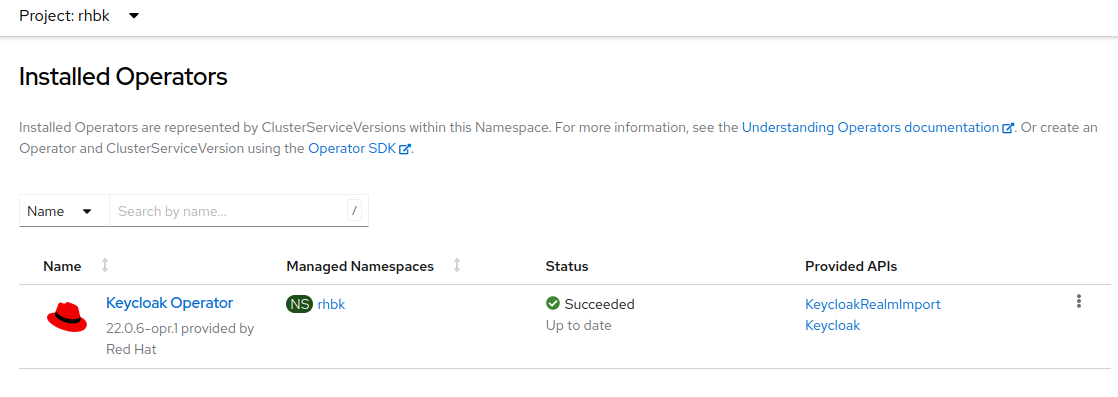
Once installed, the Keycloak Operator should appear in the list of installed operators, accessible from the Operators menu under Installed Operators.
Keycloak requires certain prerequisites (unless started in start-dev mode), which we will now install and configure.
Let’s set up the database that Keycloak will rely on. For this workshop, we’ll use a PostgreSQL database.
-
Deploy the database instance:
-
Create the secrets:
oc -n rhbk create secret generic keycloak-db-secret \
--from-literal=username=keycloak \
--from-literal=password=keycloak
The YAML file already includes the keycloak username and password for the database, which is sufficient for workshop purposes.
In a production environment, you must securely define these fields and store them in a secret.
|
-
Deploy the Red Hat build of Keycloak instance:
| For this workshop, the Keycloak instance is configured with plain HTTP enabled, and strict hostname resolution disabled. In production, TLS configuration and proper hostname setup are required. |
After deploying and confirming that the Keycloak instance is running successfully, you can access the administration console. The default credentials are randomly generated during deployment. Retrieve them using the following commands:
-
Obtain and decode the generated secrets:
oc -n rhbk get secret example-keycloak-initial-admin -o jsonpath='{.data.username}' | base64 --decode
oc -n rhbk get secret example-keycloak-initial-admin -o jsonpath='{.data.password}' | base64 --decode| In production environments, it is strongly recommended to change the default credentials and enable multi-factor authentication for enhanced security. |
-
Access the administration console using the retrieved credentials.
Deploying an Identity Management (IdM/FreeIPA) on Red Hat OpenShift
This section explains how to install FreeIPA, an Identity Management (IdM) solution that combines Linux, 389 Directory Server, MIT Kerberos, NTP, DNS, and Dogtag Certificate System.
FreeIPA is the upstream project of Red Hat Identity Management.
Later in this workshop, we will integrate Red Hat build of Keycloak with IdM/FreeIPA.
To get started, remain logged in to your Red Hat OpenShift cluster and, for convenience, select the previously created kc project.
Follow the steps below to deploy a FreeIPA instance on Red Hat OpenShift.
# Export the image to be deployed
export IMG=quay.io/freeipa/freeipa-openshift-container:4.9.8
export IMG_BASE=${IMG}
# Clone the repository and deploy the roles and SCC
# Alternatively, a remote build can be performed instead of cloning the repository
git clone https://github.com/freeipa/freeipa-openshift-container.git
cd freeipa-openshift-container/
kustomize build deploy/admin | oc create -f -
# Create the OpenShift template and deploy it
make template-create
make template-new-appTake note of the IPA_ADMIN_PASSWORD and IPA_DM_PASSWORD values displayed in the terminal; they will be required later.
Open the FreeIPA administration console to verify that access and credentials are functioning correctly.